Why Ciders Have Higher Sugar Than Some Other Drinks
Ciders generally have higher sugar content than some other alcoholic drinks like beer or wine. This is primarily due to the natural sugars present in apples, which are the main ingredient in cider production. During the fermentation process, yeast is added to apple juice to convert sugars into alcohol. The amount of sugar in the final product depends on how long the fermentation process is allowed to continue. For sweet ciders, fermentation is stopped earlier, retaining more natural sugars.
Very often additional sugar is added to enhance sweetness, appealing to those who prefer a sweeter taste. This can be seen in many of the commercial brands available such as Bulmer’s or Somersby with some as high as 1.5x your daily recommended sugar intake per pint! If you opt for craft ciders you will often see a much lower number such as at Butford Organics where we only use the natural sugars present in cider.
Comparative Sugar Content in Popular Ciders
Here is a comparison of sugar content in some popular cider brands:
| Cider Brand | Sugar Content (per pint) | Calories (per pint) |
|---|---|---|
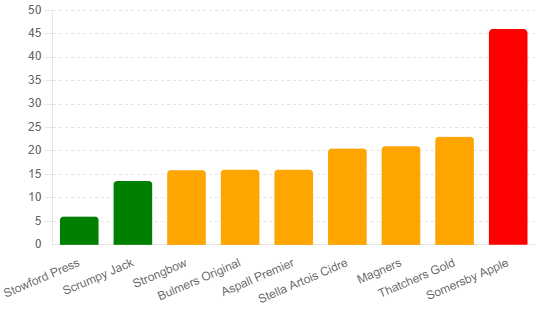
| Strongbow | 15.9g | 210 |
| Thatchers Gold | 23g | 230 |
| Magners | 21g | 235 |
| Somersby Apple | 46g | 260 |
As you can see, the sugar content varies significantly across different brands. This variation is primarily due to the fermentation process and any additional sugars added during production. This can also significantly impact the amount of calories in the cider too!
Sugar Content (in grams per pint) of popular ciders
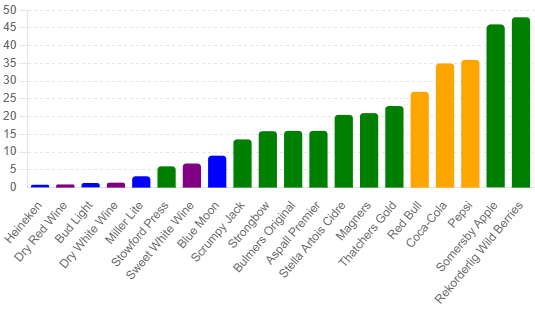
Comparing Sugar Content in Cider to other drinks
- Green = Cider
- Blue = Beer
- Purple = Wine
- Yellow = Soft Drink
Health Implications of High Sugar in Cider
Consuming high amounts of sugar from cider can have several health implications. It can contribute to weight gain, increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, and lead to other health issues such as heart disease. It’s crucial to be mindful of these risks, especially if you consume cider regularly. The NHS recommended daily allowance is 30g and as you can see many of these drinks are almost above that! 2 pints of any of the above and you are done for the day.
Low-Sugar and Sugar-Free Cider Alternatives
For those looking to enjoy cider without the high sugar content, there are low-sugar and sugar-free alternatives available. Dry ciders typically have less sugar compared to sweet ciders. Brands like Butford Organics offer dry ciders that are lower in sugar. Additionally, checking the nutritional information on labels can help identify ciders with lower sugar content.
Nutritional Information of Cider
Besides sugar, it’s important to consider the overall nutritional content of cider. Here is a typical nutritional profile for a pint of hard cider:
| Nutrient | Amount (per pint) |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 29g |
| Sugars | 23g |
| Protein | 0g |
| Sodium | 10mg |
| Vitamin C | 4.5mg |
Cider provides a substantial amount of carbohydrates and sugars, with minimal protein and sodium. Some ciders may also contain small amounts of vitamin C.
Tips for Reducing Sugar Intake
Here are some practical tips for reducing sugar intake from cider:
- Choose Dry Ciders: Opt for dry ciders, which typically have lower sugar content.
- Read Labels: Always check the nutritional information on the label to know the sugar content.
- Moderate Consumption: Limit the amount of cider you drink to reduce overall sugar intake.
Long-term Health Effects
Regular consumption of high-sugar drinks like cider can lead to long-term health effects, including obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. It’s important to balance enjoyment of cider with a mindful approach to its sugar content and overall health impact.





